Phosphorylation of ATG18a by BAK1 Suppresses Autophagy and Attenuates Plant Resistance against Necrotrophic Pathogens
AuThor:Bao Zhang, Lu Shao, Jiali Wang, Yan Zhang, Xiaoshuang Guo, Yujiao Peng, Yangrong Cao, Zhibing Lai
Autophagy. 2021 Sep. 17(9). 2093-2110
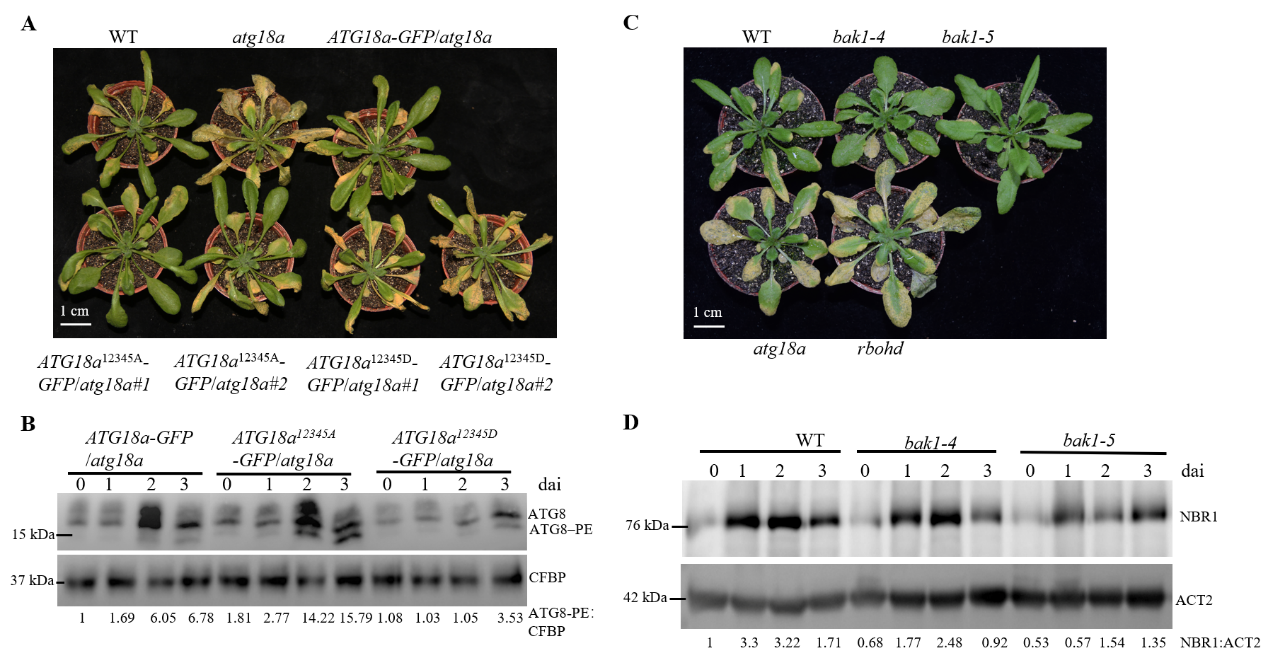
Abstract:Autophagy is critical for plant defense against necrotrophic pathogens, which causes serious yield loss on crops. However, the post-translational regulatory mechanisms of autophagy pathway in plant resistance against necrotrophs remain poorly understood. In this study, we report that phosphorylation modification on ATG18a, a key regulator of autophagosome formation in Arabidopsis thaliana, constitutes a post-translation regulation of autophagy, which attenuates plant resistance against necrotrophic pathogens. We found that phosphorylation of ATG18a suppresses autophagosome formation and its subsequent delivery into the vacuole, which results in reduced autophagy activity and compromised plant resistance against Botrytis cinerea. In contrast, overexpression of ATG18a dephosphorylation-mimic form increases the accumulation of autophagosomes and complements the plant resistance of atg18a mutant against B. cinerea. Moreover, BAK1, a key regulator in plant resistance, was identified to physically interact with and phosphorylate ATG18a. Mutation of BAK1 blocks ATG18a phosphorylation at four of the five detected phosphorylation sites after B. cinerea infection and strongly activates autophagy, leading to enhanced resistance against B. cinerea. Collectively, the identification of functional phosphorylation sites on ATG18a and the corresponding kinase BAK1 unveiled how plant regulates autophagy during resistance against necrotrophic pathogens.
DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1810426