Profiling Plant Histone Modification at Single-cell Resolution Using snCUT&Tag
Author: Weizhi Ouyang,Shiping Luan,Xu Xiang,Minrong Guo,Yan Zhang,Guoliang Li,Xingwang Li
Plant Biotechnol J. 2022 Mar. 20(3):420-422.
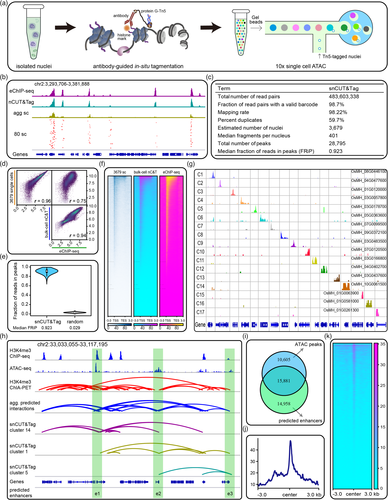
Abstract: Chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing (ChIP-seq) with population cells or tissues yields ensemble epigenomic profiles that only represent the population average, which eliminates cell-to-cell epigenetic heterogeneity. Chromatin immunocleavage with sequencing (ChIC-seq) that based on antibody-guided chromatin cleavage under targets is a practical alternative to ChIP-seq. Many single-cell ChIC-based methods, such as scChIC-seq , CUT&Tag , CoBATCH, ACT-seq , and 10x scCUT&Tag , have been developed and applied to study cell-type profiling, developmental trajectory, epigenetic heterogeneity, and transcriptional regulation in animals. However, due to the existence of cell walls, it is difficult to obtain single cells in plants. On the other hand, the existing scChIC methods require many single-cell barcoding procedures after tagmentation, which might lead to some DNA leakage and reduced mapping efficiency. Hence, a robust single-cell ChIC-seq method for plant epigenomic research is required emergently. In our previous study, we developed a rapid ChIC-based chromatin profiling protocol, nucleus CUT&Tag (nCUT&Tag). Here, we combined the nCUT&Tag assay with 10x Single Cell ATAC, developing an easy-to-use single-nucleus CUT&Tag (snCUT&Tag) method in rice.
Full Article:https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13768